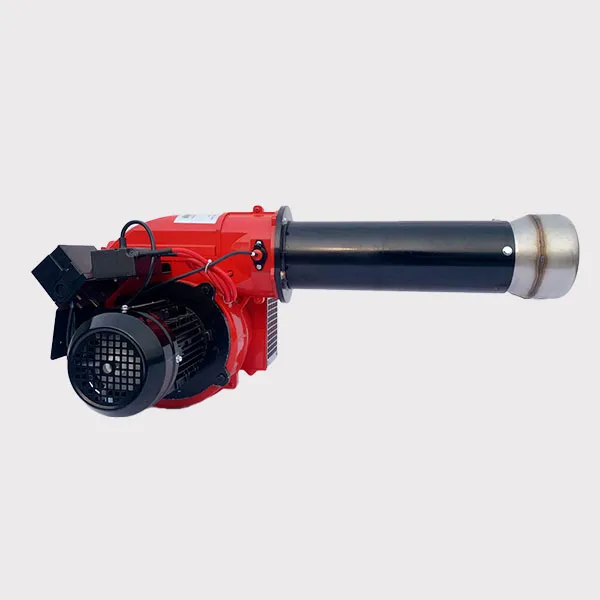
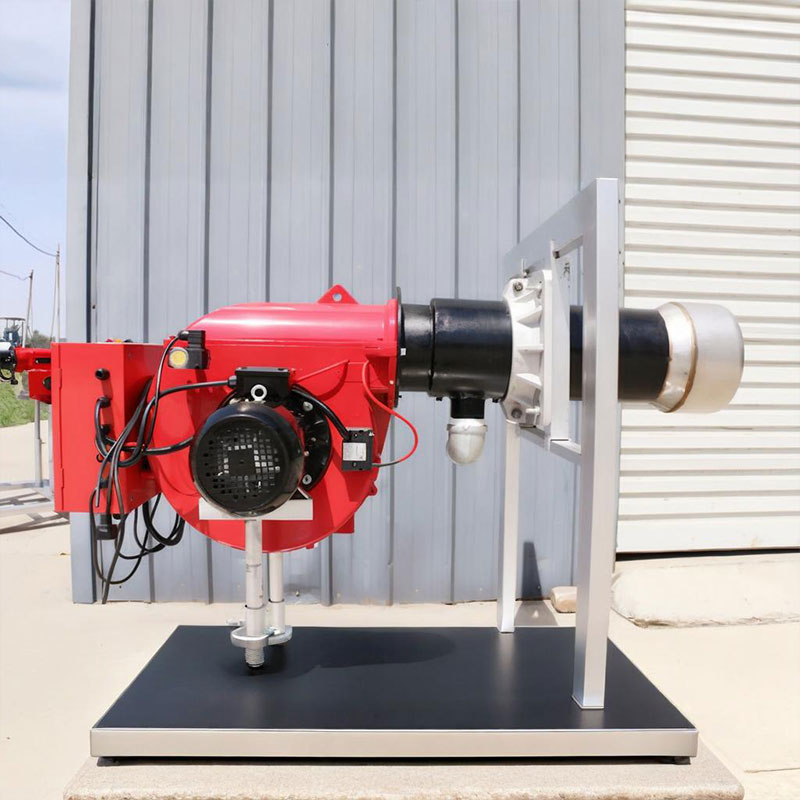
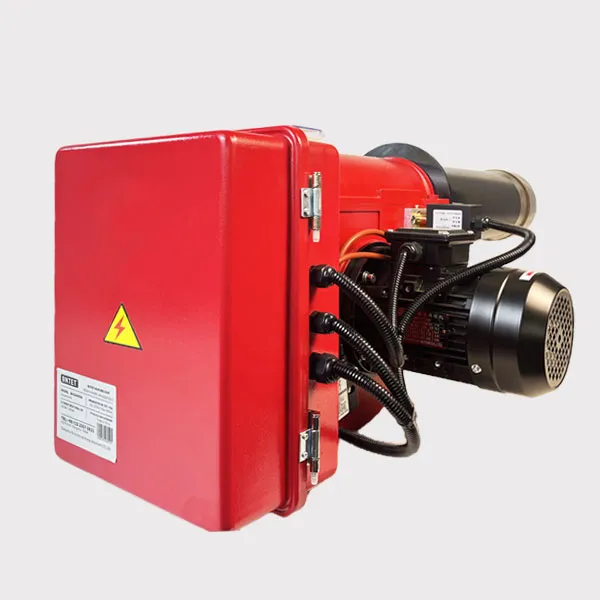
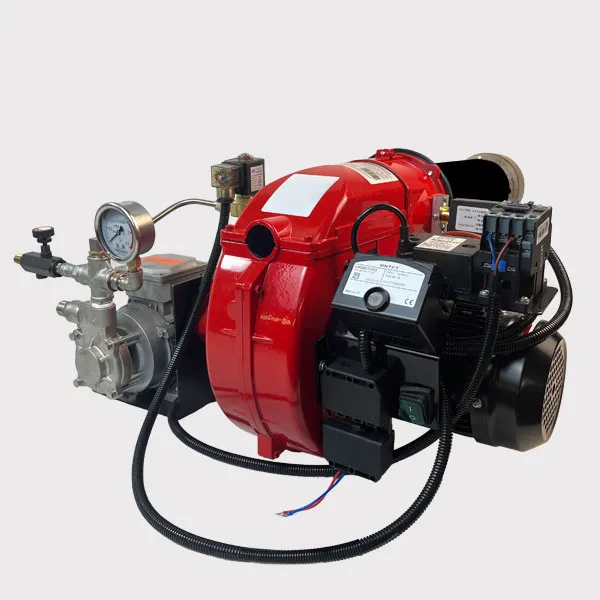
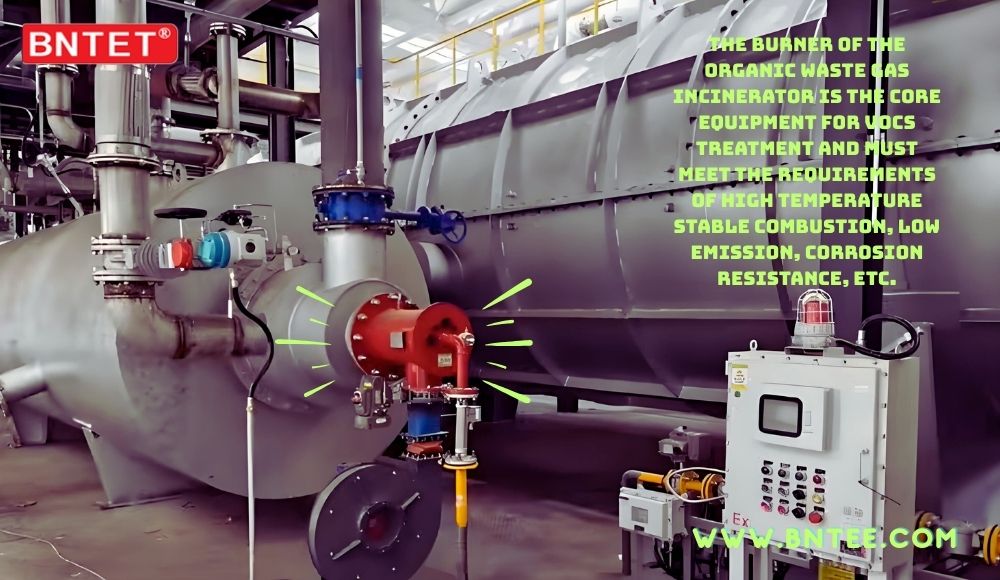
What is the VOC Incinerator Burner
2025-05-22 10:07:27
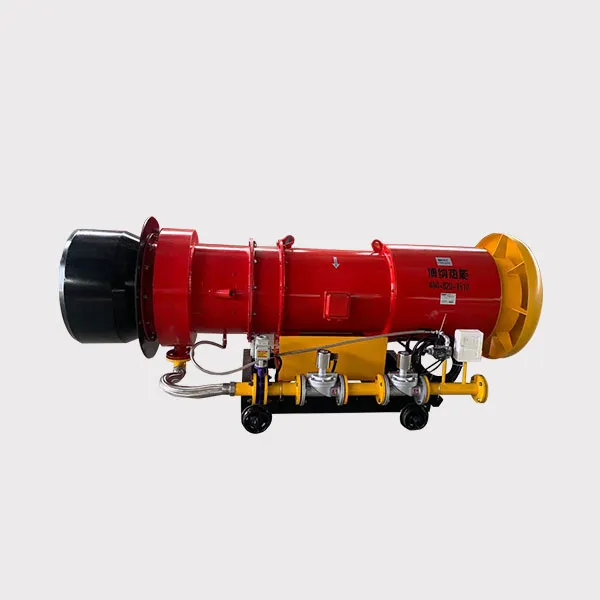
The organic waste gas incinerator burner is a critical component used for treating volatile organic compounds (VOCs). By high-temperature combustion (typically 750–1200°C), it decomposes harmful organic substances (e.g., benzene, formaldehyde, acetone) into CO₂ and H₂O, meeting environmental emission standards.

I. Core Functions of Organic Waste Gas Incinerator Burners
Efficient VOC Destruction
The combustion temperature must exceed the auto-ignition point of VOCs (e.g., benzene: 560°C, toluene: 535°C).
Destruction and removal efficiency (DRE) is typically required to be ≥99% (complying with EPA, EU, and other regulations).
Thermal Energy Recovery
Some incinerators are equipped with heat exchangers to recover waste heat for preheating exhaust gases or factory heating.
Low Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) Emissions
Technologies such as staged combustion and flue gas recirculation (FGR) are used to control NOx generation.
II. Types of Organic Waste Gas Incinerators and Corresponding Burners
Based on the combustion method, they are mainly classified into three types:
| Incinerator Type | Burner Characteristics | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Oxidizer (TO) | Direct high-temperature combustion (800–1200°C), requiring high-power burners. | High-concentration VOCs (>5% LEL). |
| Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO) | Uses ceramic heat exchangers to preheat exhaust gas; burners operate intermittently (energy savings: 30–70%). | Medium-to-low concentration VOCs (100–2000 ppm). |
| Catalytic Oxidizer (CO) | Low-temperature catalytic combustion (300–500°C), requiring lower burner power. | Low-concentration VOCs (<100 ppm), requires a catalyst. |
III. Technical Requirements for Organic Waste Gas Incinerator Burners
High-Temperature and Corrosion Resistance
Materials must withstand acidic exhaust gases (e.g., VOCs containing Cl or S); commonly uses 310S stainless steel or ceramic linings.
Precise Air-Fuel Ratio Control
Requires PLC + oxygen sensors to dynamically adjust the gas/air ratio for complete combustion.
Flame Stability
High turndown ratio (e.g., 10:1) to adapt to fluctuations in exhaust gas concentration.
Low NOx Design
Uses FGR (flue gas recirculation) or premixed combustion technology, controlling NOx emissions to <50 mg/m³.
Safety Protections
Explosion-proof design (ATEX certification), flameout protection, and exhaust gas concentration monitoring interlocks.
IV. Key Roles of Burners in VOC Treatment
Startup Phase
The burner preheats the combustion chamber to operating temperature (e.g., RTO requires preheating to 800°C).
Operation Phase
Direct combustion incinerators: Continuously provide high-temperature flames to decompose VOCs.
RTO/CO: Auxiliary heating to compensate for insufficient exhaust gas calorific value.
Emergency Situations
When VOC concentration is too low, the burner supplements heat to maintain destruction efficiency.
V. Key Considerations for Selection
Exhaust Gas Characteristics
Concentration, composition (halogen/sulfur content requires special materials), and flow rate.
Incinerator Type
RTO uses intermittent regenerative burners, while TO requires high-power continuous burners.
Energy Efficiency and Emissions
Prioritize models with waste heat recovery or low-NOx combustion technology.
Brand and After-Sales Service
International brands: Eclipse, Maxon, Weishaupt ,BNTET(high reliability).
Conclusion
Organic waste gas incinerator burners are core equipment for VOC treatment, requiring high-temperature stability, low emissions, and corrosion resistance. When selecting a burner, factors such as exhaust composition, concentration, and incinerator type must be considered to ensure compliance with local environmental regulations (EU’s IED Directive).