What is RTO regenerative incinerator burner
2025-06-11 10:10:33
The RTO (Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer) burner is a core component of VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) waste gas treatment systems. It utilizes regenerative ceramic beds to recover heat, enabling highly efficient combustion (destruction efficiency ≥99%) with ultra-low energy consumption. Its key feature is the alternating cycle of combustion and heat regeneration, where exhaust gases are heated to 800–1000°C to decompose VOCs into CO₂ and H₂O.
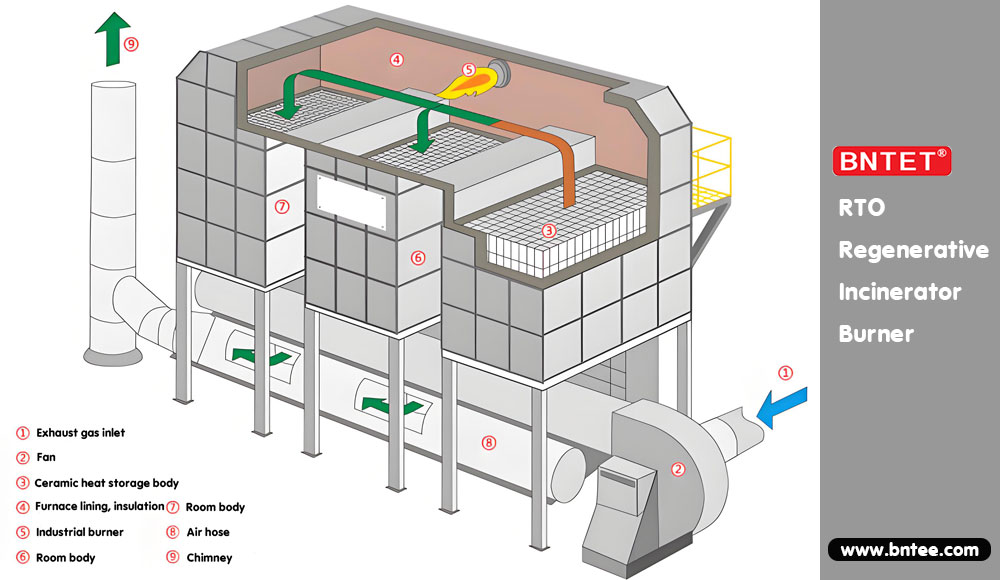
I. Working Principle of RTO Burners
Heat Regeneration-Combustion Cycle
Combustion Phase:
Exhaust gas passes through Ceramic Bed A, preheating to near combustion temperature (700–900°C).
The burner supplements heat, raising the gas temperature to 800–1000°C for complete VOC destruction.
High-temperature flue gas transfers heat to Ceramic Bed B before being discharged at low temperature (<150°C).
Switching Phase (every 1–3 minutes):
Gas flow reverses: Bed B preheats incoming gas while Bed A stores heat, with the burner adjusting flame intensity.
Energy-Saving Core
The ceramic beds recover >95% of waste heat, reducing energy consumption by 50–70% compared to direct combustion.
II. Core Components of RTO Burners
| Component | Function | Technical Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Burner Unit | Provides high-temperature flames to assist VOC combustion. | High-temperature resistance (≥1200°C), low-NOx design. |
| Ceramic Heat Beds | Store and release heat (honeycomb or pelletized ceramics). | Thermal shock resistance, high surface area (≥500 m²/m³). |
| Valve System | Controls gas flow direction (four-way or butterfly valves). | Fast response (<1 sec), high sealing performance. |
| Control System | Manages temperature, switching sequence, and safety interlocks. | PLC + O₂ sensors, supports auto/manual modes. |
III. Technical Features of RTO Burners
Ultra-Low Energy Consumption
Requires minimal supplemental fuel (e.g., natural gas), ideal for low-concentration VOCs (100–2000 ppm).
High Destruction Efficiency
Combustion temperature ≥800°C, VOC destruction rate ≥99%, compliant with EPA/EU standards.
Low NOx Emissions
Utilizes staged combustion or Flue Gas Recirculation (FGR), keeping NOx below <50 mg/m³.
Adaptability to Complex Gases
Handles corrosive components (e.g., sulfur, halogens) with materials like 310S stainless steel.
IV. RTO Burner vs. Other Incineration Technologies
| Parameter | RTO Burner | Thermal Oxidizer (TO) | Catalytic Oxidizer (CO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Temp. | 800–1000°C | 800–1200°C | 300–500°C (with catalyst) |
| Energy Use | Very low (heat recovery >95%) | High (continuous burning) | Moderate |
| VOC Concentration | 100–2000 ppm | >5000 ppm | <500 ppm |
| NOx Generation | Low (FGR technology) | High | Lowest |
V. Key Selection Criteria
Exhaust Gas Flow Rate: Determines RTO size (e.g., 10,000 Nm³/h requires matching burner capacity).
VOC Composition: Corrosive gases (e.g., chlorine/sulfur) demand anti-corrosion design.
Emission Standards: Strict regions may require additional SCR systems for NOx control.
Brand Selection:
International: Durr, Eisenmann, Anguil ,BNTET(high-precision control).
VI. FAQs
Q: Why are RTO burners more fuel-efficient than TO?
A: Ceramic beds recover waste heat to preheat incoming gas, minimizing supplemental fuel needs.
Q: Do RTO burners require frequent maintenance?
A: Ceramic beds need annual inspection for dust buildup; burner nozzles require replacement every 2 years; valves need regular lubrication.
Q: Can RTOs handle high VOC concentrations?
A: Yes, but requires LEL monitoring to prevent explosions (typically designed for ≤25% LEL).
Conclusion
RTO regenerative burners, with their heat recovery + intermittent combustion, are among the most energy-efficient VOC treatment technologies, especially for continuous, low-to-medium concentration emissions. Selection must consider exhaust characteristics, flow rate, and regulations, prioritizing suppliers with proven case studies.